Detailed classification of casting
- Share
- Issue Time
- Sep 30,2019
Summary
Detailed Classification of Casting

Detailed Classification of Casting
Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is usually poured into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowed to solidify.
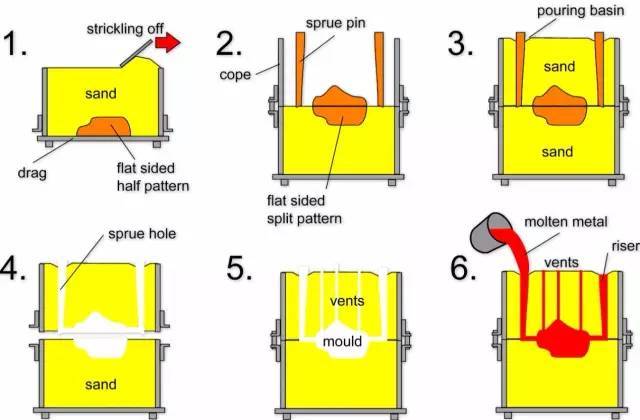
No. 1 Sand Casting
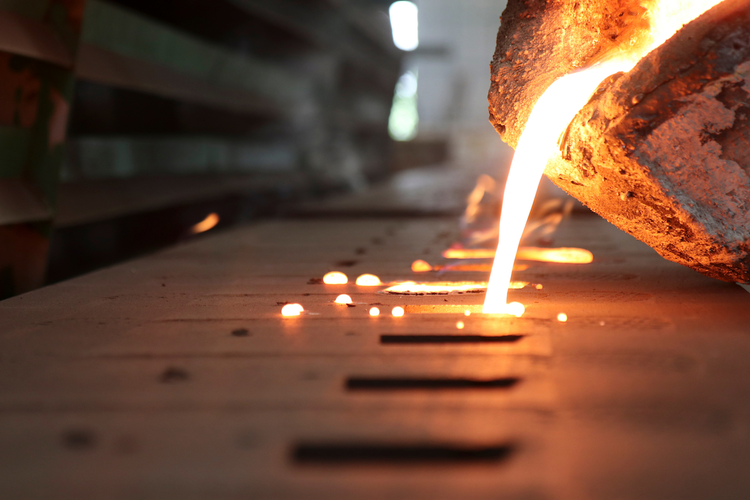

Sand casting, also known as sand molded casting, is a metal casting process characterized by using sand as the mold material. Most of metal like steel, stainless steel, etc. could produce by sand casting.
Technical Process:
Technical features:
1. Suitable for making complex shapes, especially blanks with complex internal cavities.
2. Wide adaptability and low cost.
3. For some materials with poor plasticities, such as cast iron, sand casting is the forming process for manufacturing parts or blanks.
Application:
Castings for engine cylinder block, cylinder head, crankshaft, etc.
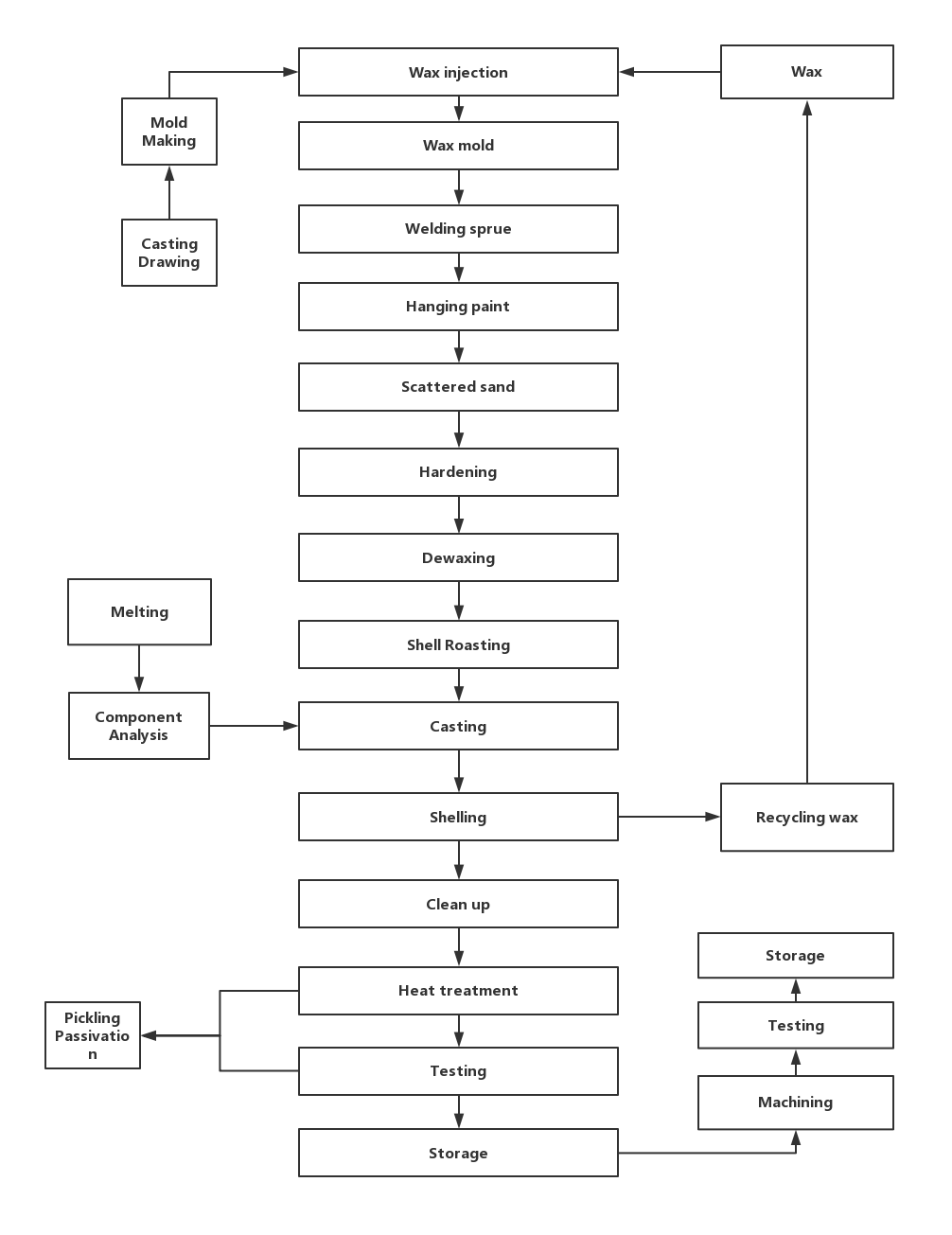
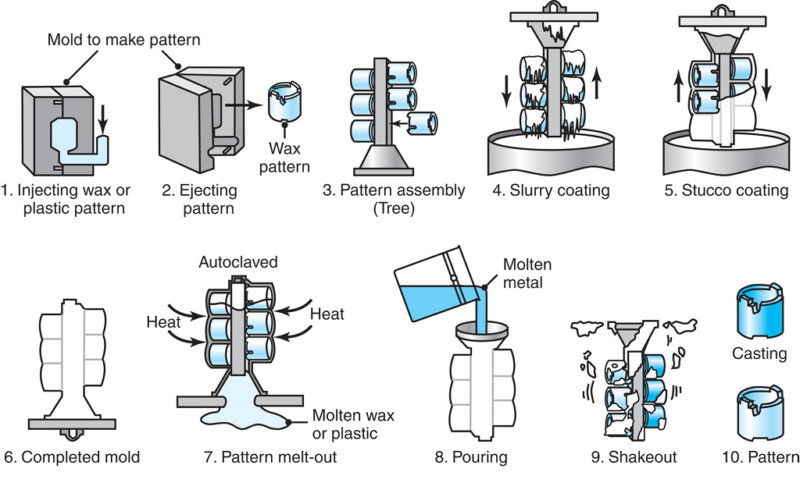
No. 2 Investment casting:

A technique for making small, accurate castings in refractory alloys using a mold formed around a pattern of wax or similar material which is then removed by melting. It is an industrial process based on lost-wax casting, one of the oldest known metal-forming techniques.
Technical Process:
Technical features:
Advantage:
1. High dimensional accuracy and geometric accuracy;
2. High surface roughness;
3. It is capable of casting castings with complex appearances, and the alloys cast are not limited.
Disadvantages:
Complicated procedures and high cost
Application:
It is suitable for the production of small parts with complex shapes, high precision requirements, or difficult to perform other processing, such as blades of turbine engines.
No. 3 Die casting

Die casting is a metal casting process that is characterized by forcing molten metal under high pressure into a mold cavity. The mold cavity is created using two hardened tool steel dies which have been machined into shape and work similarly to an injection mold during the process.
Technical Process:
Technical features:
Advantage:
High-speed production
Dimensional accuracy and stability
Strength and weight
Multiple finishing techniques
Simplified Assembly
Disadvantages:
Not applicable for high melting point metals and alloys (eg. steels)
Large parts cannot be casted.
High die cost.
Too long lead time.
Some gases may be entrapped in form of porosity.
Application:
Die casting is most suitable for casting medium sized parts with complex details. Die-casting is the largest casting technique that is used to manufacture consumer, commercial and industrial products like automobiles, toys, parts of sink faucet, connector housing, gears, etc. Most die castings are done from non-ferrous metals like aluminum, magnesium, etc.
No. 4 Low-pressure casting
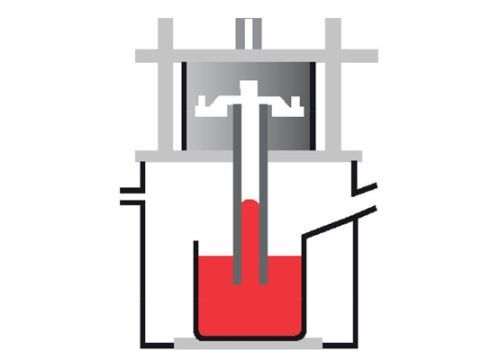
Low pressure casting is a process in which a ceramic tube is connected to a steel die above and extends into a furnace of molten metal below. ... Once the casting has solidified the air pressure is reduced allowing the rest of the metal still in liquid form in the tube to recede back into the furnace.
Low-pressure process:
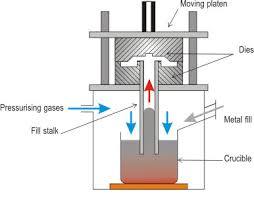
Advantages:
1. Possible to cast fairly complex products than feasible by gravity die casting, due to precision tooling used for casting.
2. High production efficiency can be achieved as the whole process is almost completely automated.
3. The casted part can have a very good surface finish by post finishing.
4. Can reach a very small wall thickness, the injected liquid metal under high pressure can filled the cavity easily.
5. Better mechanical properties and tighter dimensional tolerances than other casting processes.
6. Economical both for small or larger volume production.
Disadvantages:
1. There might have set-up cost for small volume quantities parts, but this cost is low nowadays in China
2. Limitation by the casting machine capacity.
3. It is not suitable for all materials because of the limitations of the alloys used must have a low melting point.
4. Heat treatment is difficult & porosity is common.
Application
This process was created for the production of axially symmetrical parts such as car wheels.
However, by employing sand cores within the die, it is also well suited to producing parts with hollow sections and complex geometries.
No. 5 Centrifugal casting

A casting method in which a molten metal is poured into a rotating mold and filled with a mold under centrifugal force to solidify and form.
Technical Process
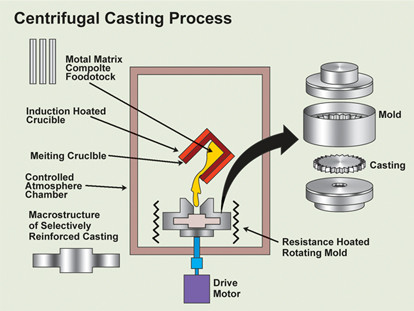
Technical features:
Advantage:
1. There is almost no metal consumption of the gating system and the riser system, which improves the process yield;
2. The core can be used in the production of hollow castings, so the metal filling ability can be greatly improved when producing long tubular castings;
3. The casting has high density, less defects such as pores and slag inclusion, and high mechanical properties;
4, easy to manufacture cylinders, sets of composite metal castings.
Disadvantage:
1. There are certain limitations when used to produce shaped castings;
2. The diameter of the inner hole of the casting is not accurate, the surface of the inner hole is rough, the quality is poor, and the machining allowance is large;
3. Castings are prone to segregation of specific gravity.
Application:
Centrifugal casting is used to produce cast pipes earlier. At home and abroad, centrifugal casting processes are used in metallurgy, mining, transportation, irrigation and drainage machinery, aviation, national defense, automotive and other industries to produce steel, iron and non-ferrous carbon alloy castings. Among them, the production of castings such as centrifugal cast iron pipes, internal combustion engine cylinder liners and bushings is more common.
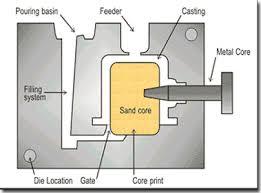
No. 6 gravity die casting
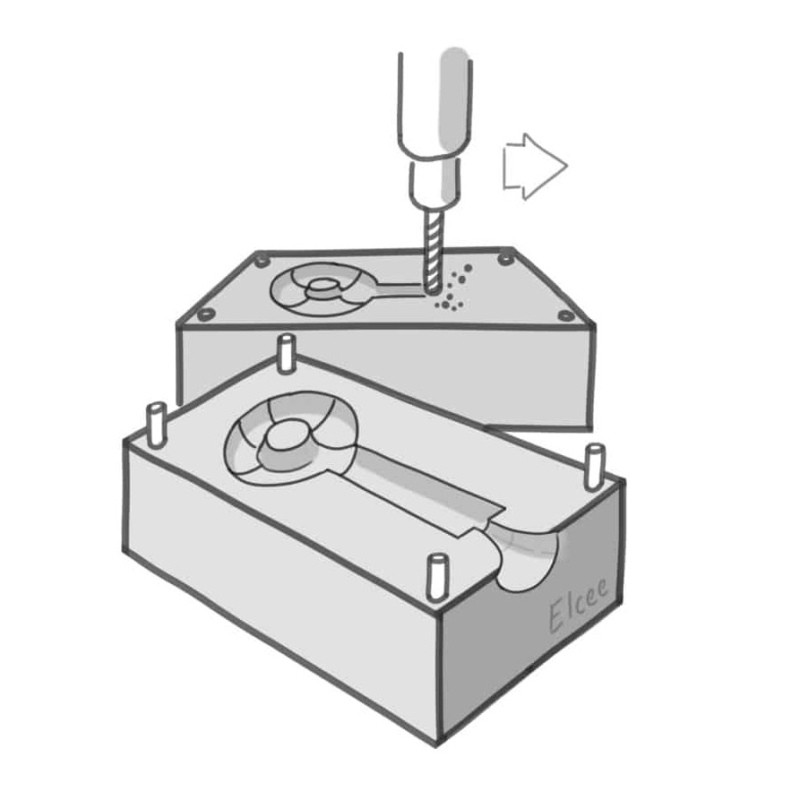
Gravity die casting refers to a molding method in which a liquid metal is filled with a metal mold under the action of gravity and cooled and solidified in a mold to obtain a casting.
Technical Process:
Technical features:
Advantage:
1. The thermal conductivity and heat capacity of the metal type are large, the cooling rate is fast, the casting structure is dense, and the mechanical properties are about 15% higher than the sand casting.
2. It can obtain castings with higher dimensional accuracy and lower surface roughness, and has good quality stability.
3, because of the use and rarely use sand core, improve the environment, reduce dust and harmful gases, reduce labor intensity.
Disadvantages:
1. The metal type itself has no gas permeability, and certain measures must be taken to derive the air generated by the cavity and the gas generated by the sand core;
2. The metal type has no repellent property, and the casting is prone to crack when solidified;
3. The metal type has a long manufacturing cycle and high cost. Therefore, only when a large number of batch production can show good economic results.
Application:
Metal casting is suitable for mass production of non-ferrous alloy castings such as aluminum alloys and magnesium alloys with complex shapes, as well as castings and ingots for the production of steel and metal.
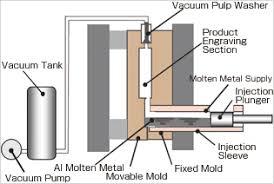
No. 7 Vacuum die Casting

The air holes and dissolved gases in die casting are eliminated or significantly reduced by removing the air from the die cavity during die casting
Thus the advanced die casting technology can improve the mechanical properties and surface quality of die castings.
Technological Process:
Technical features:
Advantage:
Eliminate or reduce air holes in die casting parts, enhance mechanical properties and surface quality of die castings, improve coating performanc.
Reduce the adverse pressure of the cavity, alloys with low specific pressure and poor casting properties can be used, it is possible to die cast larger castings with small machines.
Improved filling conditions, A thin casting can be die-casteds
Disadvantage:
Mold sealing structure is complex, difficult to manufacture and install, so the cost is higher
Vacuum die casting is not properly controlled, the effect is not very conspicuous.
No. 8 Squeezing Die Casting
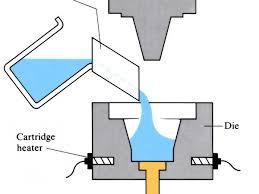
It is a method of making liquid or semi-solid metal solidify and flow forming under high pressure to directly obtain workpiece or workblank. It has the advantages of high utilization rate of liquid metal, simple process and stable quality. It is an energy saving metal forming technology with potential application prospect.
Technical Process:
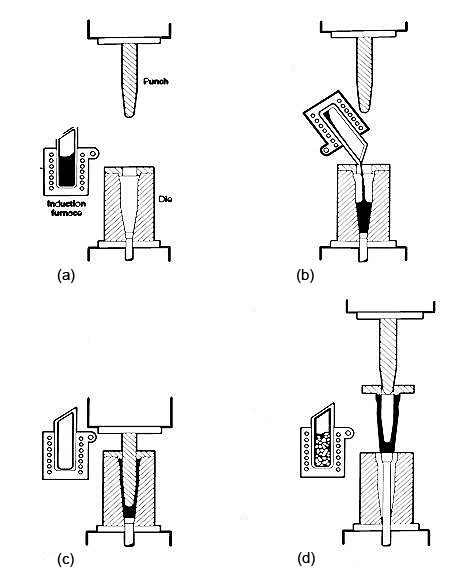
Classification:
Direct Squeezing Casting:
Spray paint, pouring alloy, mold clamping, feedstock, mold filling, inflating, pressure maintaining, decompression, mold splitting, Blank demolding, restoration.
Indirect Squeezing Casting:
Sparypaint, Mold Clamping, Feedstock, Mold Filling, Inflating, Pressure maintaining, Decompression, Mold splitting, Blank demoulding, Restoraion.
Technical Feature:
It can eliminate internal defects such as air hole, shrinkage cavity and porosity
Low surface roughness, High dimensional accuracy.
It can prevent the generation of casting crack
Easy to realize mechanization and automation
Application:
Can be used to produce various types of alloys. Such as aluminum alloy, zinc alloy, copper alloy, ductile iron and so on.
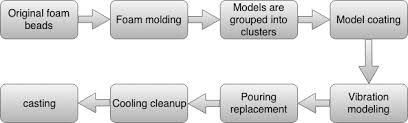
No. 9 Lost foam casting (also known as solid mold casting):
It is a new casting method that makes paraffin or foam models similar to casting size and shape bond together to form model clusters, brush with fire-resistant coating and dry them, bury them in dry quartz sand and vibrate them, pour them under negative pressure, gasify the model, occupy the position of the model with liquid metal, and solidify and cool the casting.
Technical process:
Technical Feature:
High casting accuracy. No sand core, Reduced processing time.
No parting surface, flexible design, High degree of freedom
CP (Cleaner Production), non-pollution;
Reduce investment and production costs
Application:
Suitable for all kinds of precision castings with complex structure, there is no limit on the types of alloy and the quantity of production.Such as gray cast iron engine box, high manganese steel elbow.
No. 10 Continuous casting

It is an advanced casting method. The principle is that the molten metal is continuously poured into a special metal mold called a crystallizer, and the solidified (crusted) casting is continuously pulled out from the other end of the crystallizer to obtain a casting of any length or specified length
Technical process:
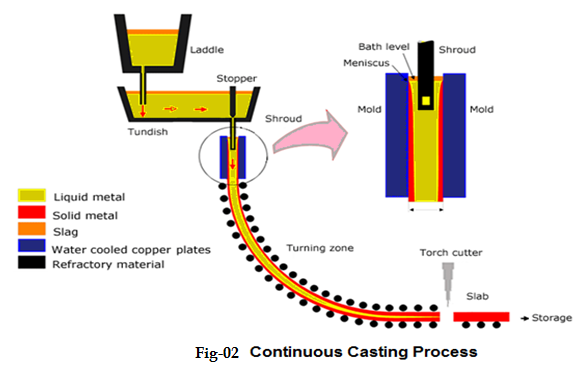
Technical feature:
As the metal is cooled quickly, crystal densification, well-closed formation, Good mechanical performance
Save the metal, increase yield.
Simplifies the process, exempt from modelling and other procedures, thus reducing labor intensity; The production area required has also been greatly reduced;
Continuous casting production is easy to achieve mechanization and automation, improve production efficiency
Application:
Continuous casting can be used to cast A long casting with constant section shape of steel iron, copper alloy, aluminum alloy, magnesium alloy, etc. Such as ingots, slabs, billets, pipes and so on.